
If this symbol is defined, it indicates that the system has the POSIX.2 C compiler command, c89. The GNU C library always defines this as 1, on the assumption that you would not have installed it if you didn't have a C compiler. The GNU C Library. Node:File Index, Previous:Variable Index, Up:Top. Program and File Index-lbsd-compat: Process Group Functions, Feature Test Macros. The GNU C Library version 2.34 is now available. Item posted by Carlos O'Donell on Mon 02 Aug 2021 03:57:01 AM UTC. The GNU C Library The GNU C Library version 2.34 is now available. The GNU C Library is used as the C library in the GNU system and in GNU/Linux systems, as well as many other systems that use Linux as the kernel.
Table of Contents
How To Install Gnu C Library On Ubuntu
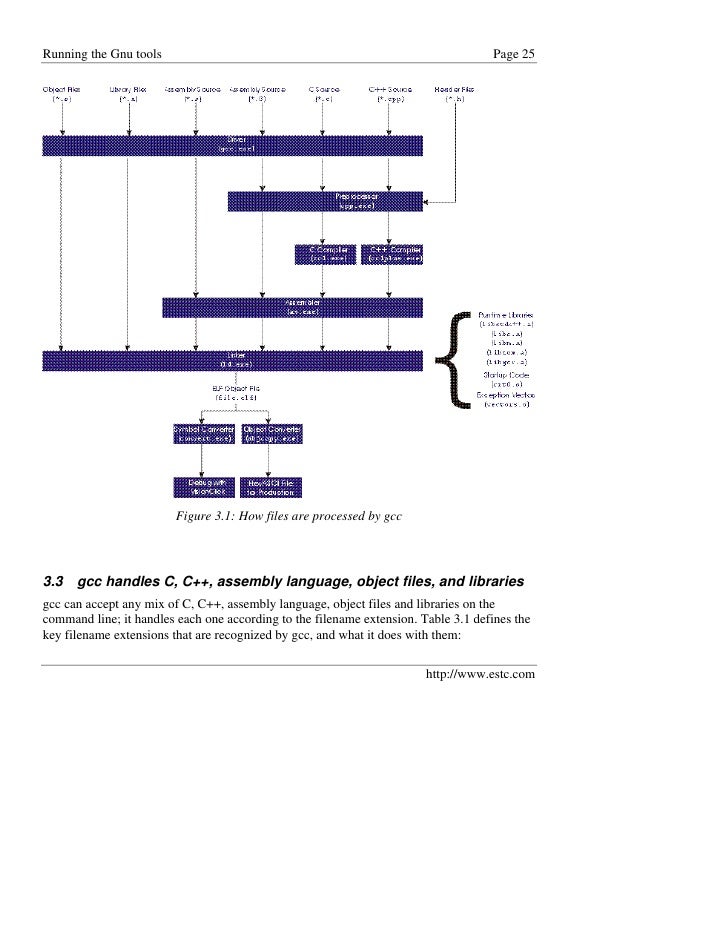
Gnu C Library On Demand
- I. Introduction
- 1. Status
- Implementation Status
- C++ 1998/2003
- Implementation Status
- Implementation Specific Behavior
- C++ 2011
- Implementation Specific Behavior
- C++ 2014
- Implementation Specific Behavior
- Filesystem TS
- C++ 2017
- Implementation Specific Behavior
- Parallelism 2 TS
- C++ 2020
- C++ TR1
- Implementation Specific Behavior
- C++ TR 24733
- C++ IS 29124
- Implementation Specific Behavior
- License
- The Code: GPL
- The Documentation: GPL, FDL
- Bugs
- Implementation Bugs
- Standard Bugs
- 2. Setup
- Prerequisites
- Configure
- Make
- 3. Using
- Command Options
- Headers
- Header Files
- Mixing Headers
- The C Headers and
namespace std - Precompiled Headers
- Macros
- Dual ABI
- Troubleshooting
- Namespaces
- Available Namespaces
- namespace std
- Using Namespace Composition
- Linking
- Almost Nothing
- Finding Dynamic or Shared Libraries
- Experimental Library Extensions
- Concurrency
- Prerequisites
- Thread Safety
- Atomics
- IO
- Structure
- Defaults
- Future
- Alternatives
- Containers
- Exceptions
- Exception Safety
- Exception Neutrality
- Doing without
- Compatibility
- With
C - With
POSIXthread cancellation
- With
- Debugging Support
- Using g++
- Debug Versions of Library Binary Files
- Memory Leak Hunting
- Non-memory leaks in Pool and MT allocators
- Data Race Hunting
- Using gdb
- Tracking uncaught exceptions
- Debug Mode
- Compile Time Checking
- II. Standard Contents
- 4. Support
- Types
- Fundamental Types
- Numeric Properties
- NULL
- Dynamic Memory
- Additional Notes
- Termination
- Termination Handlers
- Verbose Terminate Handler
- 5. Diagnostics
- Exceptions
- API Reference
- Adding Data to
exception
- Use of errno by the library
- Concept Checking
- 6. Utilities
- Functors
- Pairs
- Memory
- Allocators
- Requirements
- Design Issues
- Implementation
- Interface Design
- Selecting Default Allocation Policy
- Disabling Memory Caching
- Using a Specific Allocator
- Custom Allocators
- Extension Allocators
- auto_ptr
- Limitations
- Use in Containers
- shared_ptr
- Requirements
- Design Issues
- Implementation
- Class Hierarchy
- Thread Safety
- Selecting Lock Policy
- Related functions and classes
- Use
- Examples
- Unresolved Issues
- Acknowledgments
- Traits
- 7. Strings
- String Classes
- Simple Transformations
- Case Sensitivity
- Arbitrary Character Types
- Tokenizing
- Shrink to Fit
- CString (MFC)
- 8. Localization
- Locales
- locale
- Requirements
- Design
- Implementation
- Interacting with 'C' locales
- Future
- Facets
- ctype
- Implementation
- Specializations
- Future
- codecvt
- Requirements
- Design
- wchar_t Size
- Support for Unicode
- Other Issues
- Implementation
- Use
- Future
- messages
- Requirements
- Design
- Implementation
- Models
- The GNU Model
- Use
- Future
- 9. Containers
- Sequences
- list
- list::size() is O(n)
- Associative
- Insertion Hints
- bitset
- Size Variable
- Type String
- Unordered Associative
- Insertion Hints
- Hash Code
- Hash Code Caching Policy
- Interacting with C
- Containers vs. Arrays
- 10. Iterators
- Predefined
- Iterators vs. Pointers
- One Past the End
- 11. Algorithms
- Mutating
swap- Specializations
- 12. Numerics
- Complex
- complex Processing
- Generalized Operations
- Interacting with C
- Numerics vs. Arrays
- C99
- 13. Input and Output
- Iostream Objects
- Stream Buffers
- Derived streambuf Classes
- Buffering
- Memory Based Streams
- Compatibility With strstream
- File Based Streams
- Copying a File
- Binary Input and Output
- Interacting with C
- Using FILE* and file descriptors
- Performance
- 14. Atomics
- API Reference
- 15. Concurrency
- API Reference
- III. Extensions
- 16. Compile Time Checks
- 17. Debug Mode
- Intro
- Semantics
- Using
- Using the Debug Mode
- Using a Specific Debug Container
- Design
- Goals
- Methods
- The Wrapper Model
- Safe Iterators
- Safe Sequences (Containers)
- Precondition Checking
- Release- and debug-mode coexistence
- Compile-time coexistence of release- and debug-mode components
- Link- and run-time coexistence of release- and debug-mode components
- Alternatives for Coexistence
- Other Implementations
- 18. Parallel Mode
- Intro
- Semantics
- Using
- Prerequisite Compiler Flags
- Using Parallel Mode
- Using Specific Parallel Components
- Design
- Interface Basics
- Configuration and Tuning
- Setting up the OpenMP Environment
- Compile Time Switches
- Run Time Settings and Defaults
- Implementation Namespaces
- Testing
- Bibliography
- 19. The mt_allocator
- Intro
- Design Issues
- Overview
- Implementation
- Tunable Parameters
- Initialization
- Deallocation Notes
- Single Thread Example
- Multiple Thread Example
- 20. The bitmap_allocator
- Design
- Implementation
- Free List Store
- Super Block
- Super Block Data Layout
- Maximum Wasted Percentage
allocatedeallocate- Questions
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Locality
- Overhead and Grow Policy
- 21. Policy-Based Data Structures
- Intro
- Performance Issues
- Associative
- Priority Que
- Goals
- Associative
- Policy Choices
- Underlying Data Structures
- Iterators
- Functional
- Priority Queues
- Policy Choices
- Underlying Data Structures
- Binary Heaps
- Using
- Prerequisites
- Organization
- Tutorial
- Basic Use
- Configuring via Template Parameters
- Querying Container Attributes
- Point and Range Iteration
- Examples
- Intermediate Use
- Querying with
container_traits - By Container Method
- Hash-Based
- Branch-Based
- Priority Queues
- Design
- Concepts
- Null Policy Classes
- Map and Set Semantics
- Distinguishing Between Maps and Sets
- Alternatives to
std::multisetandstd::multimap
- Iterator Semantics
- Point and Range Iterators
- Distinguishing Point and Range Iterators
- Invalidation Guarantees
- Genericity
- Tag
- Traits
- By Container
- hash
- Interface
- Details
- tree
- Interface
- Details
- Trie
- Interface
- Details
- List
- Interface
- Details
- Priority Queue
- Interface
- Details
- Testing
- Regression
- Performance
- Hash-Based
- Text
find - Integer
find - Integer Subscript
find - Integer Subscript
insert - Integer
findwith Skewed-Distribution - Erase Memory Use
- Text
- Branch-Based
- Text
insert - Text
find - Text
findwith Locality-of-Reference splitandjoin- Order-Statistics
- Text
- Multimap
- Text
findwith Small Secondary-to-Primary Key Ratios - Text
findwith Large Secondary-to-Primary Key Ratios - Text
insertwith Small Secondary-to-Primary Key Ratios - Text
insertwith Small Secondary-to-Primary Key Ratios - Text
insertwith Small Secondary-to-Primary Key Ratios Memory Use - Text
insertwith Small Secondary-to-Primary Key Ratios Memory Use
- Text
- Priority Queue
- Text
push - Text
pushandpop - Integer
push - Integer
push - Text
popMemory Use - Text
join - Text
modifyUp - Text
modifyDown
- Text
- Observations
- Associative
- Priority_Queue
- Acknowledgments
- Bibliography
- 22. HP/SGI Extensions
- Backwards Compatibility
- Deprecated
- 23. Utilities
- 24. Algorithms
- 25. Numerics
- 26. Iterators
- 27. Input and Output
- Derived filebufs
- 28. Demangling
- 29. Concurrency
- Design
- Interface to Locks and Mutexes
- Interface to Atomic Functions
- Implementation
- Using Built-in Atomic Functions
- Thread Abstraction
- Use
- IV. Appendices
- A. Contributing
- Contributor Checklist
- Reading
- Assignment
- Getting Sources
- Submitting Patches
- Directory Layout and Source Conventions
- Coding Style
- Bad Identifiers
- By Example
- Design Notes
- B. Porting and Maintenance
- Configure and Build Hacking
- Prerequisites
- Overview
- General Process
- What Comes from Where
- Configure
- Storing Information in non-AC files (like configure.host)
- Coding and Commenting Conventions
- The acinclude.m4 layout
GLIBCXX_ENABLE, the--enablemaker- Shared Library Versioning
- Make
- Writing and Generating Documentation
- Introduction
- Generating Documentation
- Doxygen
- Prerequisites
- Generating the Doxygen Files
- Debugging Generation
- Markup
- Docbook
- Prerequisites
- Generating the DocBook Files
- Debugging Generation
- Editing and Validation
- File Organization and Basics
- Markup By Example
- Porting to New Hardware or Operating Systems
- Operating System
- CPU
- Character Types
- Thread Safety
- Numeric Limits
- Libtool
- Testing
- Test Organization
- Directory Layout
- Naming Conventions
- Running the Testsuite
- Basic
- Variations
- Permutations
- Writing a new test case
- Examples of Test Directives
- Directives Specific to Libstdc++ Tests
- Test Harness and Utilities
- DejaGnu Harness Details
- Utilities
- Special Topics
- Qualifying Exception Safety Guarantees
- Overview
- Existing tests
- C++11 Requirements Test Sequence Descriptions
- ABI Policy and Guidelines
- The C++ Interface
- Versioning
- Goals
- History
- Prerequisites
- Configuring
- Checking Active
- Allowed Changes
- Prohibited Changes
- Implementation
- Testing
- Single ABI Testing
- Multiple ABI Testing
- Outstanding Issues
- API Evolution and Deprecation History
3.03.13.23.33.44.04.14.24.34.44.54.64.74.84.955.3
677.27.3
89101112
- Backwards Compatibility
- First
- Second
- Third
- Pre-ISO headers removed
- Extension headers hash_map, hash_set moved to ext or backwards
- No
ios::nocreate/ios::noreplace. - No
stream::attach(int fd) - Support for C++98 dialect.
- Support for C++TR1 dialect.
- Support for C++11 dialect.
Container::iterator_typeis not necessarilyContainer::value_type*
- C. Free Software Needs Free Documentation
- D. GNU General Public License version 3
- E. GNU Free Documentation License